|
|

2006年底,CAAU从来自23个国家的162个设计团队中脱颖而出,赢得香港知专设计学院(HKDI)大楼的设计项目。HKDI项目由香港职业教育处发起,旨在建造一座能面积42,000㎡,能容纳4,000名艺术与多媒体专业学生的教学楼。值得一提的是,HKDI是香港第一座由法国建筑师设计的大型建筑。
The Hong Kong Institute of Design project was won at the end of 2006 by Coldefy & Associés, Architectes Urbanistes / CAAU, winners of the two stage international competition in which 162 teams from 23 countries took part. The CAAU studio was entrusted with the task of designing the project with architectural project management of the site directed by its Hong Kong partner, P&T Group.
Intended to welcome 4, 000 students of artistic and multimedia disciplines in around 42, 000 m2, the
HKDI is commissioned by the Vocational Training Council Hong Kong.
The HKDI is the first major facility built in Hong Kong by a French architect
城市环境
The urban context
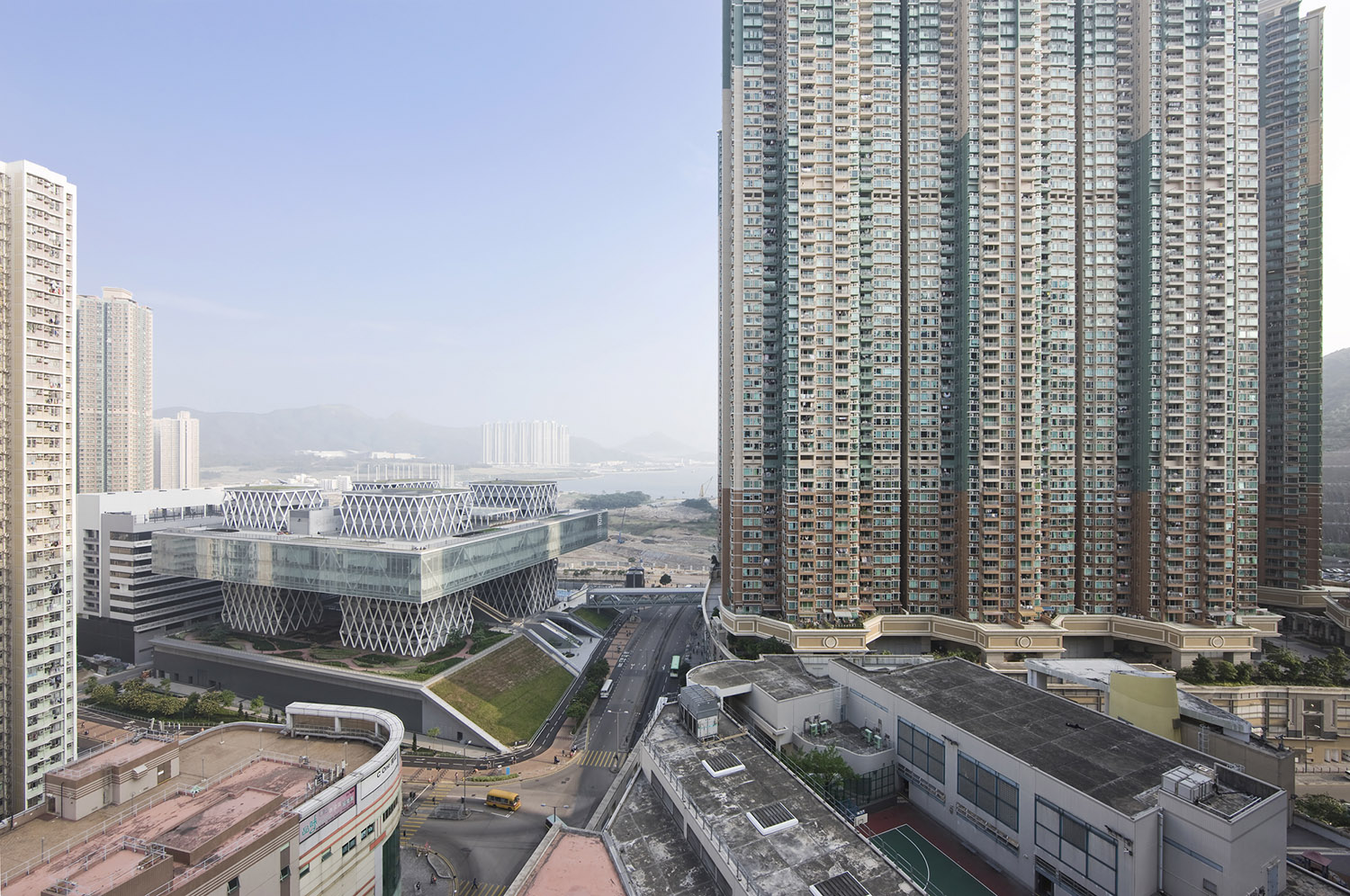
建筑位于香港岛东北部西贡区的调景岭片区,毗邻将军澳,通过地铁和巴士线与市中心相连接。虽然该区域主要用作住宅和商业用途,但绿山环绕、三面环海的自然景观处处可见。HKDI位于片区的中心,可供公众使用的运动场和报告厅为周边社区提供了聚会的场所;与此同时,在这座可以容纳4000名学生的校园内,将围绕城市空间展开不计其数的展览和活动,让整个片区活跃起来。HKDI将其所在的城市文脉转换到自身的空间演绎中来,与社会的互动被设置在多样化的底部空间内,在那里建筑的垂直性仿佛已经消失不见了;错落的高差使人可以在不同层面设想互动的方式,同时与地面建立新的联系。
The building is located in the Tiu Keng Leng area, to the north east of Hong Kong Island, in the Sai Kung district, adjacent to the Tseung Kwan O area and Junk Bay. The area is served by the metro, on the Tseung Kwan O line, 20 minutes from HK Central, and also has a bus station. Although activity there is mainly residential and commercial, nature is also very much present for the site is surrounded by green hills and the view over Junk Bay is everywhere. The building, located in the heart of the area, may provide the community with a meeting place by making its sports areas and auditoriums available; at the same time, it will bring an energy to the social life of the area by the presence of 4, 000 students within the campus, the numerous exhibitions and activities organised around the urban space it has created.
The project offers spatial reinterpretation of its built-up city context, where social interactions are teeming in the various bases of the buildings whereas they disappear vertically; the extra height provided by one part of the programme allows one to envisage interactions on different levels and creates new connections with the ground.
▼鸟瞰,bird view


▼ 入口分析,the access diagram

建筑设计
The architectural project
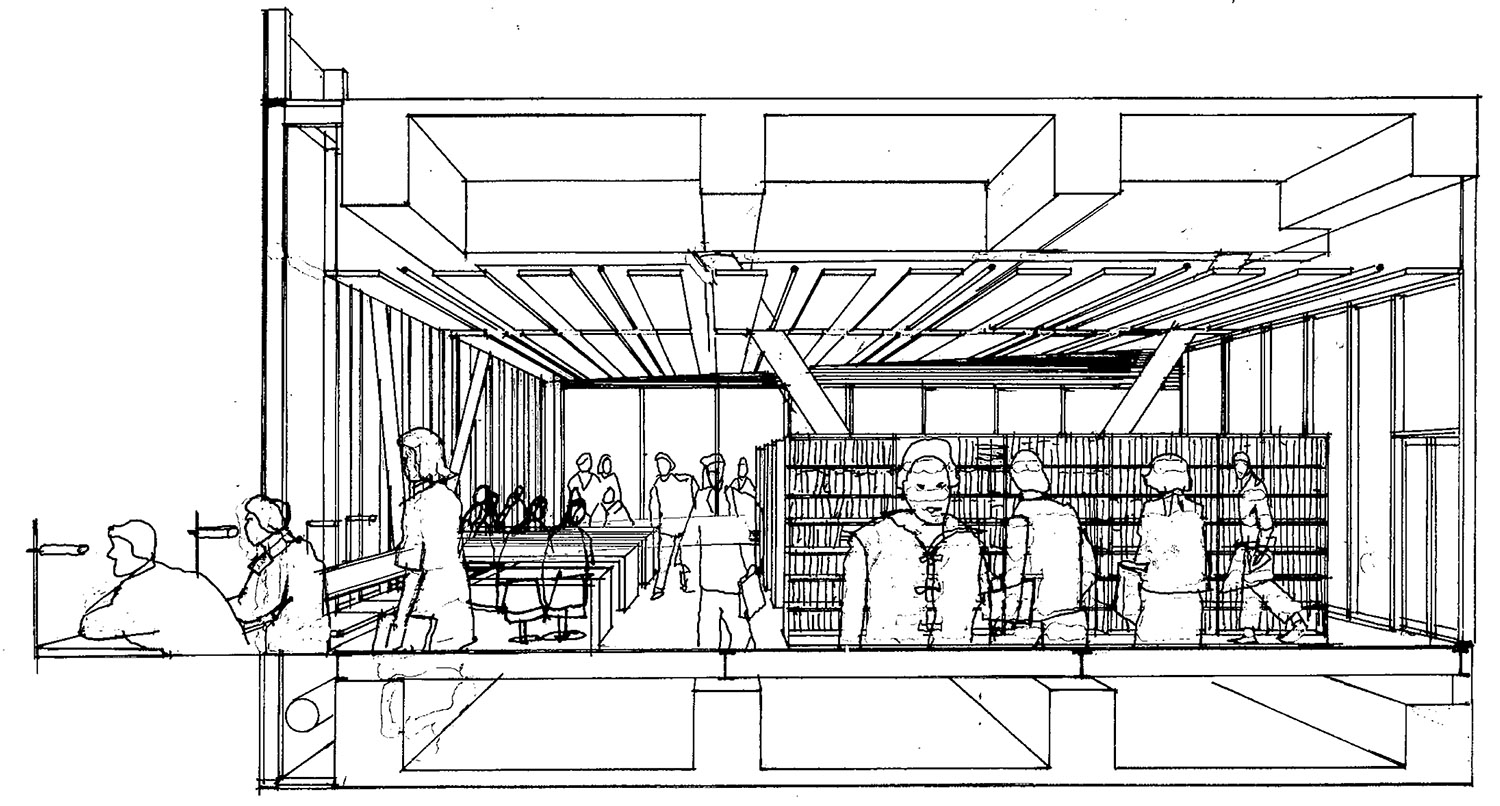
设计的概念“白纸”隐喻了无限的创意可能,也表达出项目的初衷,即未来的设计学院要汇集多种学科,并能够适应各学科的特点和发展目标。由混凝土、玻璃和钢构成的建筑,轻盈通透,展现出多样而矛盾的融合特质:既内向又外向;既谦逊又张扬;既微观又宏观,既传统又先锋,既是为特定的人群而建又欢迎每一个来访者。各个功能元素在解构、穿插、重组之后,共同为城市贡献了一座外表干净利落的建筑。灵活的,可更新的平面使得未来与邻近校园建立联系成为可能。
建筑的基座是一座巨大的“城市客厅”,加深了建筑与城市的联系。市民可以充分利用内部和外部的绿色空间,举办各种各样的聚会和交流活动,同时欣赏市郊的美丽景色。
基座上方的平台比一侧的景岭路高7m,建筑师将之设计成一道城市景观,同时也是香港一处别具特色的基础设施。基座在两个层面同城市环境发生关系——它既是一块公共空间,又是一处室外展览的场所。
基座内包括4间报告厅、一间餐厅、一间室内运动场、一间展厅及交流空间。大型的报告厅可以容纳700个座位,可用于举办大型会议、音乐会、时装秀、当代舞表演等诸多娱乐活动。基座平台由一座城市公园及运动场组成,既为学生服务,也为周围的市民提供活动场所。
Metaphor for creativity about to burst forth, the “Blank Sheet” expresses the project’s intentions :
bringing together and then presenting the multidiscipline nature and targets of the future Institute of Design. In concrete, glass and steel, its radical architecture, light and transparent, invites one to reflect on the combination of multiple and opposing situations : introversion and extroversion, modesty and exhibition, exclusivity and wide accessibility, micro and macro city, classicism and experimentation …
Each functional element, first decomposed, amalgamates and interpenetrates or cuts itself off, by offering the project an immediate clarity from the outside which is very resonant in the city. The flexible and evolutionary plan allows one to envisage future liaisons with the neighbouring campus, LWL.
The base of the building, the giant “ urban lounge “ favours meetings and exchanges, whilst taking advantage of internal and external green spaces and views of the countryside, thus fulfilling the liaison with the city.
The podium, whose gentle slope stands 7m below the King Ling Road, designed as a landscaped extrusion of the ground, directly linked to the urban environment on two levels – a common space and at the same time an external gallery – is characteristic of Hong Kong infrastructures. Open, sheltered by the platform above, it can host multiple events. The podium is made up of four auditoriums, a café, a space for exchanges with the design industry, a sports hall and an exhibition hall. For the roof, an urban park and sports grounds are available to the students and visitors from nearby. The large auditorium, with capacity for 700 seats, is intended to host conferences, seminars or classical music concerts, but also more recreational activities, fashion shows, pop music concerts, contemporary dance spectacles.
▼ 概念草图,the concept sketches

▼ 基座,the podium

▼ 基座一侧的公共报告厅,the public auditorium

▼ 展厅和运动场,the exhibition hall and the sports ground


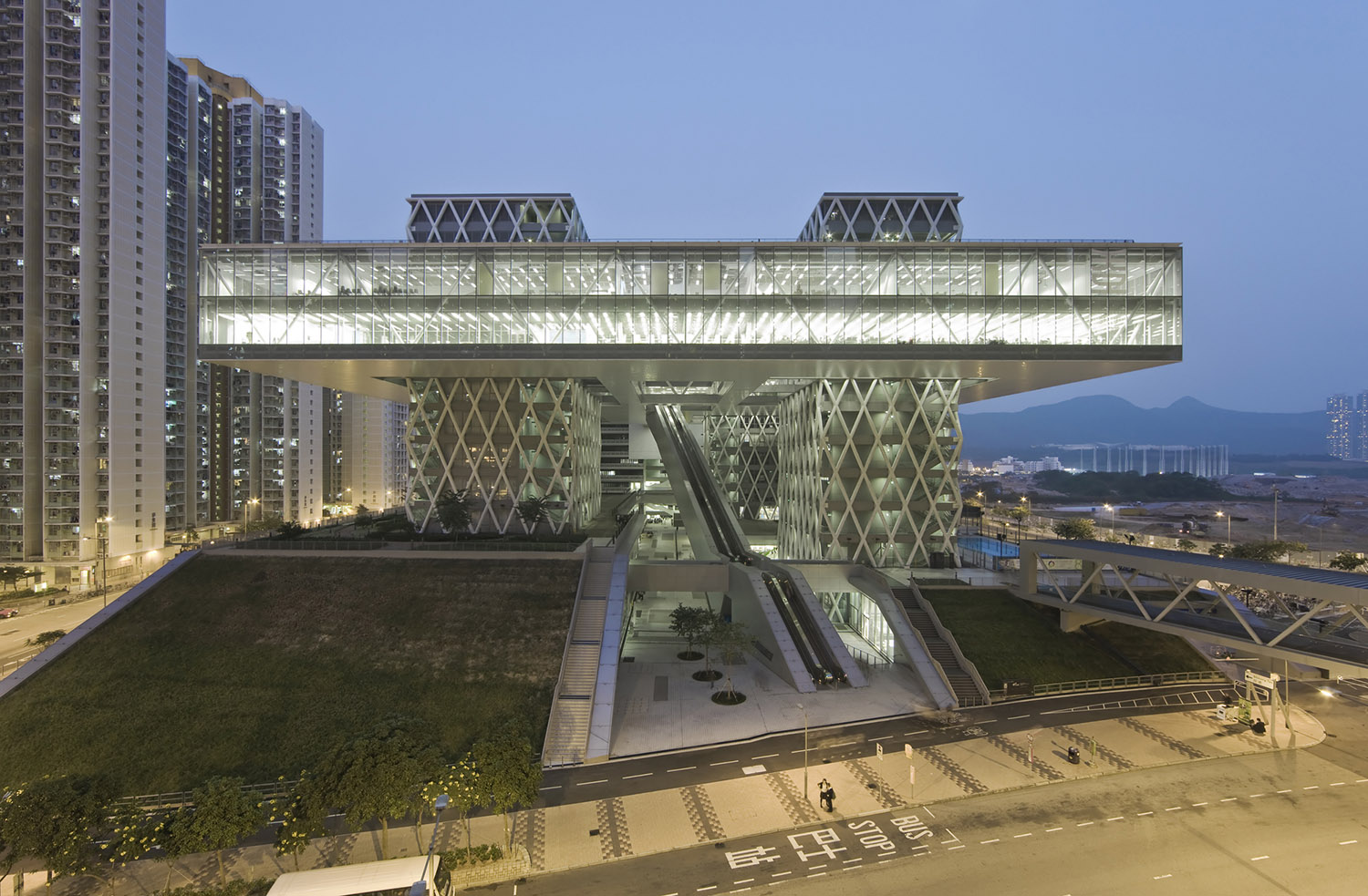
天空之城
An aerial city
建筑表面覆盖着白色丝网印花玻璃,干净利落、极简主义风格的空中体量俨然“一座空中之城”悬浮在塔楼之间。这座体量中布置着图书馆和行政办公室。体量上方可上人的屋顶花园在特别活动时对外开放。塔楼是学院的核心,它的结构和直冲云霄的体量感更加凸显了空中平台的非物质性,后者用它充满诗意的造型,向外界展示学院所具有的创造力。建筑的整体形象赋予了学院某种超越时间的特性,也让它的野心展露无遗——一座综合性的、没有知识边界的、兼具公共性与互动性的学校。而建筑本身则注定成为城市中一座明亮的灯塔。
Covered in glass which is screenprinted white, the immaculate and minimal volume of the platform, “like “an aerial city”, floats above the towers. It groups together the library, school administration offices as well as various related spaces. Its landscaped roof is accessible during exceptional events.
The towers are at once the soul of the Institute, its structure and its vertical distribution. They express the diversity and the specific nature of the disciplines represented in the Design Institute. Their appearance accentuates the platform’s immateriality, a poetic sensation and reflection of a creative environment.
This overall composition, emerging from the interpenetration of interlinked elements, defines the Institute as a timeless building and unveils its ambition of synergy, of a cutting edge school, of publicity and interactivity, destined to become a bright beacon in the city.
▼ 空中平台夜景,the night view of the platform

▼ 空中平台室内,interior of the platform

▼ 空中平台草图,the sketch of the platform
材料
The materials
混凝土、玻璃和钢,三种典型的建筑材料被运用到非典型的建造过程中来,共同打造出这座无所谓时代定义的功能主义建筑。白色的钢铁框架作为结构性表皮出现在空中平台的内侧和塔楼的外侧。平台的玻璃立面赋予它极好的通透感,这种通透感加深了建筑构件之间的张力。结构性的混凝土基座,和周遭的玻璃立面,营造出强烈的视觉和空间印象。
Concrete, glass and steel, three classic materials are implemented for a radical architectural process, a building of a different age reduced to its fundamental functions. The steel, processed into a white trellis, is used as a structural skin for both the inside of the platform and the outside of the towers. The glass of the platform gives it great permeability which strengthens the sensation of tension between the architectural elements.
The structural cement of the podium is combined with glazed facades to exceed mere functionality and create a strong visual and spatial impact.
结构
The construction system
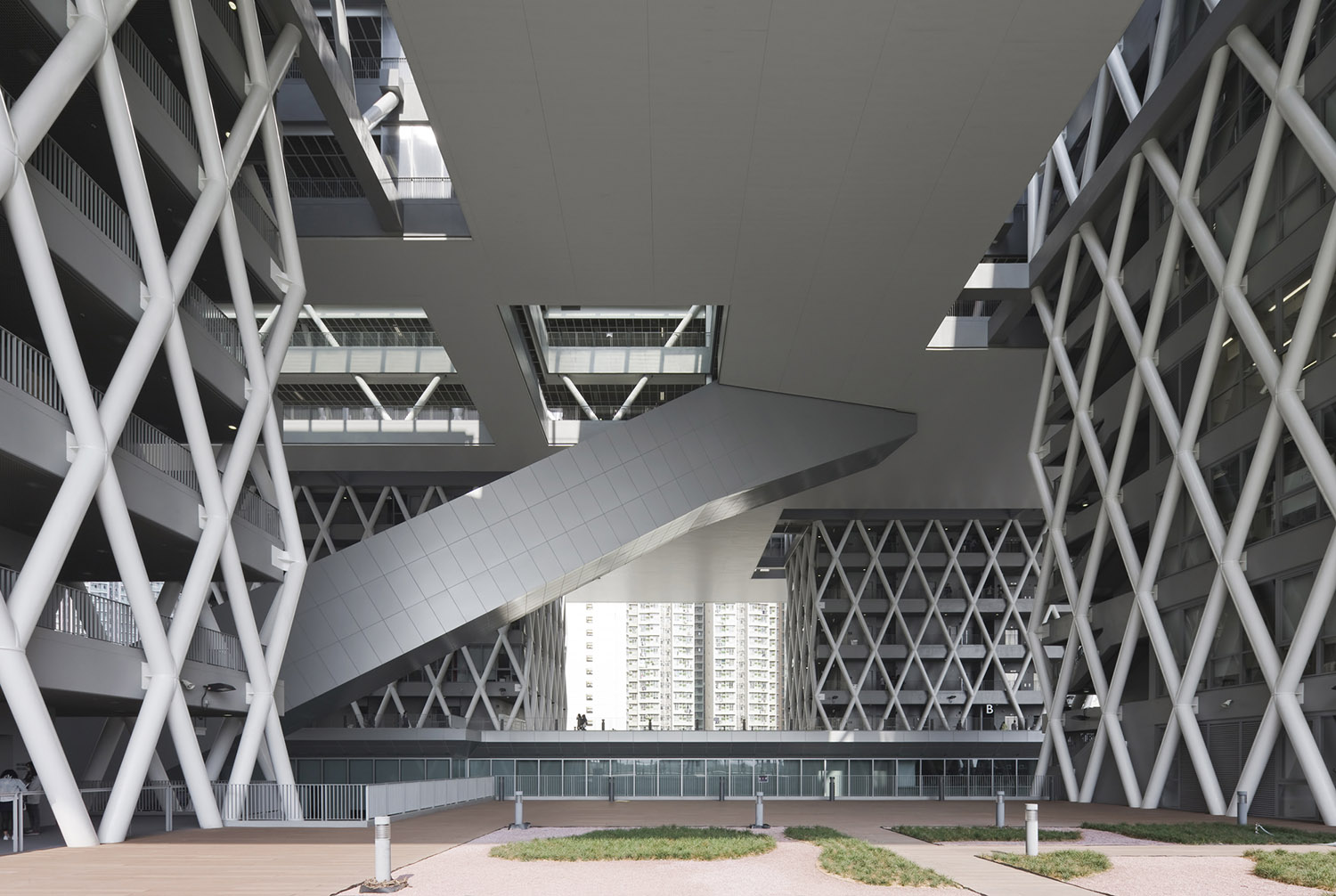
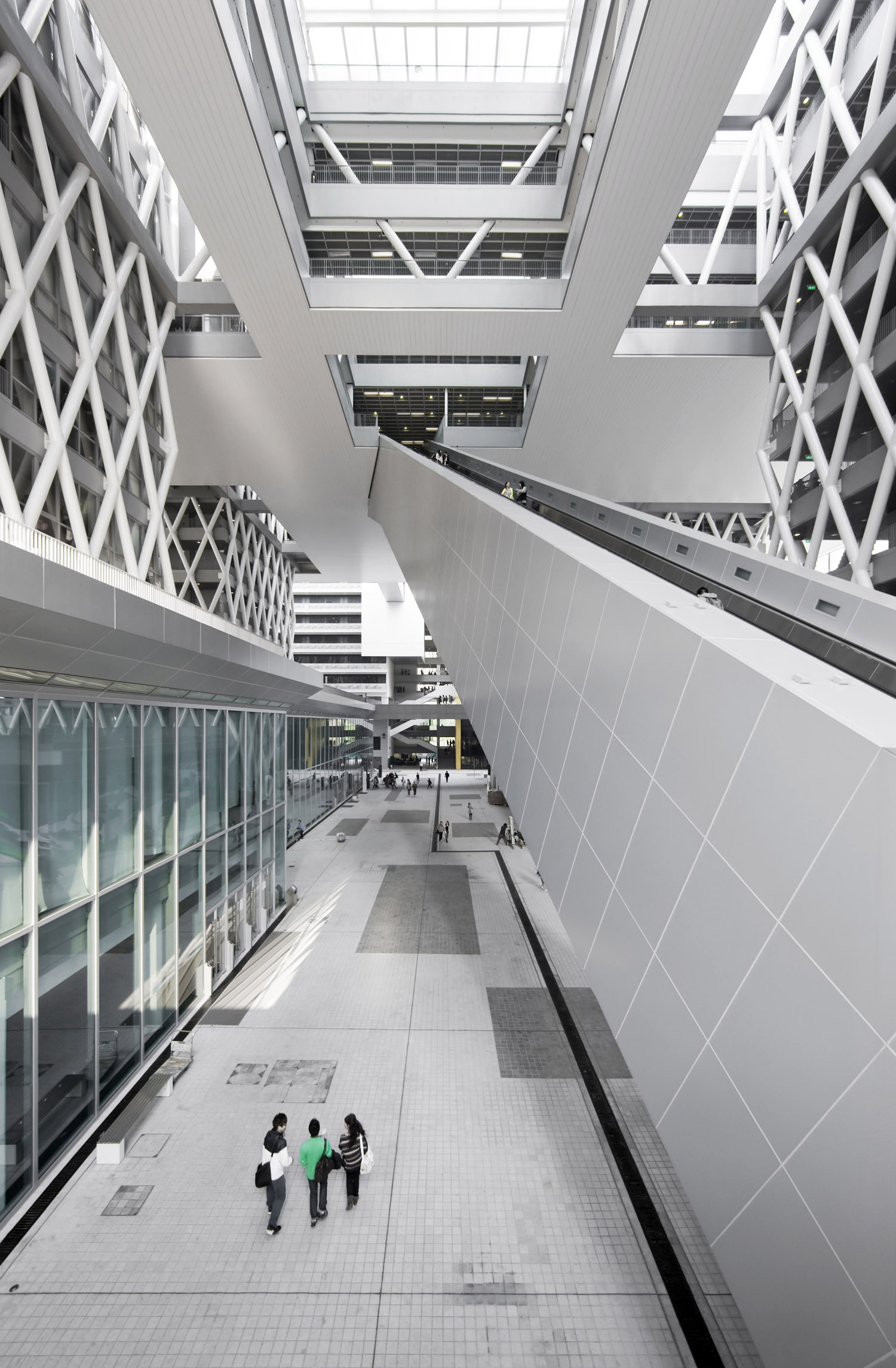
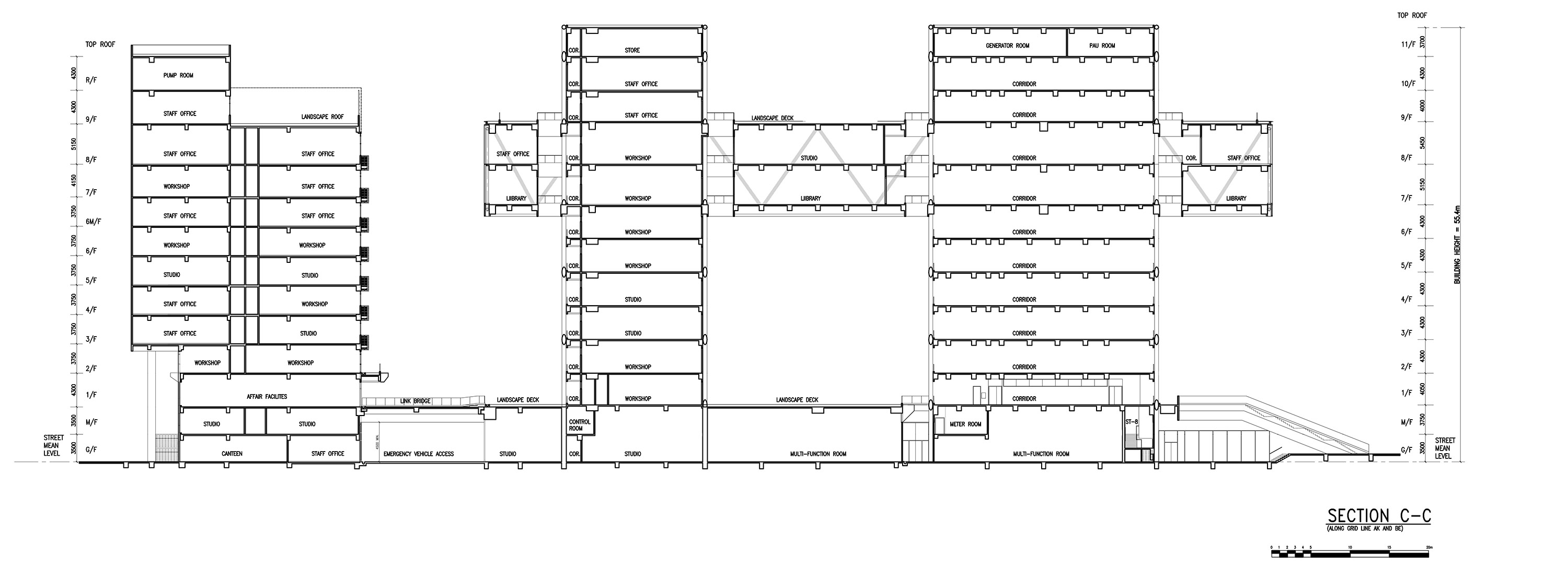
垂直的“斜交格构”式的钢结构与传统的混凝土梁板体系共同支撑起整座建筑。“斜交格构”系统具有出众的横向刚度,支撑起空中的体量和跨度达60m的扶梯构件。外置的刚结构使HKDI成为香港一座具有先锋意义的建筑。这一创新的结构体系由钢筋混凝土和钢结构组合而成,上部的框架结构使用的是施加了预应力及后张应力的菱形钢梁,下部的框架结构则是由钢筋混泥土构成,二者共同作用支撑起跨度达100mX100m的空中平台。而使平台从塔楼的立面悬挑出去的水平结构则由正交的均匀分布在楼板上钢筋混凝土梁构成。综合的结构体系不仅赋予了建筑足够的刚性和抗风性能,还降低了造价。建筑师还在该项目中设计了香港最长的跨度达60m的扶梯系统,后者完全由三维钢框架支撑,不涉及任何直接的支撑结构。除以上提到的基建工作外,建筑师还进行动态分析,以保证扶梯引擎引起的颤动不会给用户带来任何不适。独立于设计之外,空中体量的搭建工作是建筑师最为关心的问题。他们做了充分的测试以保证结构不会有任何风险,且能在合理的时间内完成。建筑师对几种建造方式做了透彻的研究,其中包括在地面预先将主框架搭建好,再通过重型起重设备将其提升至最终的位置。在评估了施工风险、难度和成本之后,建筑师最终决定采用现场组装的方式。为了将现场预组装的工作量减少到最小,在主体结构建成之后,再将大多数次级结构构件安装上去,之后将脚手架拆除。
The overall stability of the towers is ensured by a vertical steel trellis structure called “diagrid”, equipped with a conventional beam-slab floor system in reinforced concrete.
This “diagrid” system in steel offers excellent lateral rigidity supporting both the floating platform and the framework of the escalator which spans a length of 60m. HKDI is a pioneering project in Hong Kong, due to the choice of a peripheral steel trellis structural system.
An innovative structure in composite reinforced concrete /steel trellis – with upper frameworks which are pre-stressed and post-stressed, diagonal beams in steel and lower frameworks in reinforced concrete – has been introduced and developed in order to support the floating platform which spans an area of 100 m x 100 m. The composite trellises are either simply supported, or placed overhanging from the towers in steel trelliswork.
Uniformly distributed on the floating platform in two orthogonal directions, they are used to support the beam-slab floor system in reinforced concrete.
This composite structure not only provides the floating platform with rigidity and sufficient resistance, it also meant construction costs could be optimised, in so far as the budget set by the client was not exceeded. The implementation of the project also required that the architects design a 60 m long escalator structure – the longest escalator in Hong Kong – supported by a three-dimensional steel structure without any immediate support. Over and above the general design of the infrastructure work, the dynamic analysis carried out meant there could be a guarantee that the vibrations caused by the escalator engines do not cause discomfort to users. Independently of the design, the ability to construct the floating platform has been, from the initial creative stage, one of the major concerns. Sufficient tests were carried out in order to ensure that the proposed structure would be built without any risk and within a reasonable timeframe. Several construction methods have been researched, including pre- assembly of the main frame of the floating platform on the ground and then having it elevated into final position using heavy lifting appliances. After assessing risks, difficulty and costs linked to construction in this way, the in situ manufacturing method with complex on site assembly procedures was adopted. Finally, to reduce on site pre- assembly work to a minimum, the majority of secondary structural elements of the floating platform were built after completion of the main structures and removal of the scaffolding which supported them.
▼ 外露的“斜交格构”式的钢结构,the peripheral steel trellis structure with “diagrid” system

▼ 扶梯,the escalator



▼ 手绘扶梯构造,the construction drawing of the escalator

▼ 1F

▼ 地面层平面图,the ground floor

▼ 4F

▼ 7F

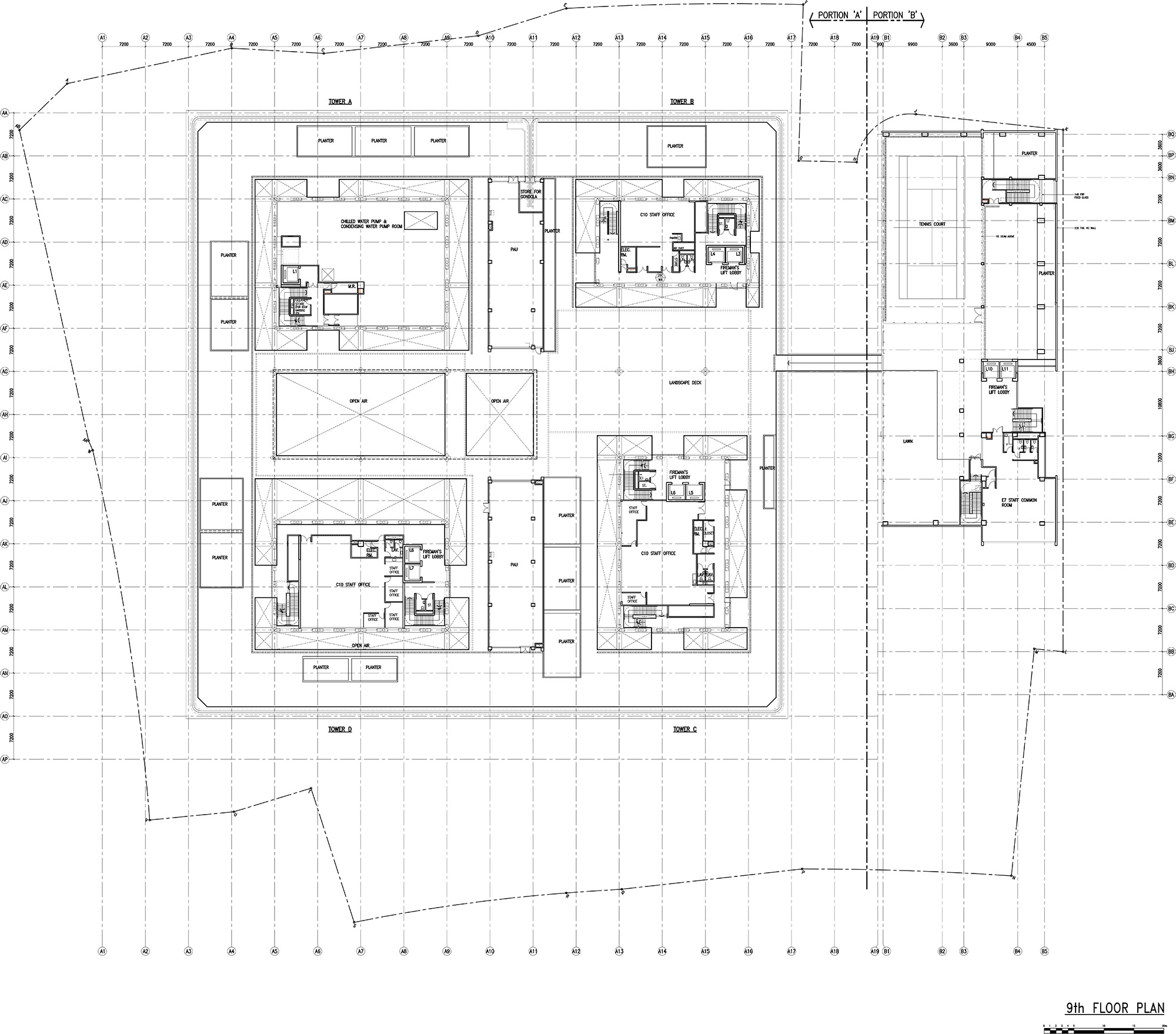
▼ 9F
▼ 剖面图 section

|
|